Stainless Steel Storage Tanks
For more than fifty years, Tate Metalworks, Inc. has been an industry leading supplier of both API-650 and API-620 storage tanks and ASME pressure vessels fabricated and erected from stainless steel materials. Our stainless steel storage tanks and pressure vessels can be found in near limitless applications and industries throughout the United States and the world. We have supplied storage and process solutions to the specialty chemicals, plastic recycling, petrochemical, petroleum, pulp and paper, minerals and mining, lithium production, power generation, pharmaceutical, food and beverage industries, and many more. Our expertise is not only the welding of the material but the handling, cleaning, and erection of the stainless steel tanks to safeguard the material’s corrosion resistance properties and assure our clients years of reliable process serviceability.
Key Features & Benefits of Stainless Steel Tanks
Stainless steel storage tanks are renowned for their exceptional corrosion resistance and hygienic properties, making them a popular choice for industries where cleanliness and longevity are paramount. The most common grades of stainless steel in tank construction are dual certified 304/304L and 316/316L. Our tanks are manufactured using high-grade stainless steel alloys, ensuring maximum resistance to corrosion from the harsh environmental conditions they are exposed to.
Some of the key benefits to utilizing stainless steel materials for storage tanks include:
Material strength and durabilityStainless steel is chosen for its robustness and resistance to corrosion, making it suitable for storing both corrosive and non-corrosive liquids. It withstands extreme temperatures and maintains structural integrity over time. |
Hygienic propertiesStainless steel tanks are easy to clean and maintain, which is crucial for industries like food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and healthcare where cleanliness is paramount. |
VersatilityThey can store a wide range of substances including water, chemicals, food products, pharmaceuticals, and beverages without compromising the quality or safety of the stored material. |
CustomizationTanks can be customized in size, shape, and features to meet specific storage needs, whether for large-scale industrial applications or smaller residential installations. |
Longevity and cost-effectivenessWhile stainless steel tanks may have a higher initial cost compared to some other materials, their durability and minimal maintenance requirements often result in lower long-term costs. |
Environmental considerationsStainless steel is recyclable, which supports sustainability efforts and reduces environmental impact compared to other non-recyclable materials. |
Regulatory complianceThey often meet stringent industry standards and regulations for safety, quality, and environmental protection, ensuring compliance with legal requirements. |
Corrosion resistanceStainless steel is renowned for its exceptional corrosion resistance, which is one of its primary advantages in various applications. |
Key Factors to Stainless Steel's Corrosion Resistance
- Chromium content: Stainless steel contains a significant amount of chromium (typically at least 10.5%), which forms a passive oxide layer on the surface of the material. This oxide layer is extremely thin (only a few nanometers thick) but dense and stable, preventing further oxidation and corrosion of the underlying metal.
- Passivation: When stainless steel is exposed to oxygen-rich environments, such as air or water, the chromium in the alloy reacts with oxygen to form this protective oxide layer. This process is called passivation and occurs naturally, enhancing the material's corrosion resistance.
- Other alloying elements: Besides chromium, stainless steel often includes other alloying elements such as nickel, molybdenum, and sometimes nitrogen. These elements can further enhance corrosion resistance, particularly in harsh environments or when exposed to specific corrosive substances.
- Types of stainless steel: There are different grades and types of stainless steel, each tailored for specific applications based on their alloy composition. For instance, austenitic stainless steels (such as 304 and 316 grades) are highly corrosion-resistant and widely used in industries like food processing, pharmaceuticals, and marine environments.
- Resistance to specific corrosive agents: Stainless steel exhibits resistance to various corrosive agents, including acids, alkalis, chloride solutions (saltwater), and atmospheric conditions. The exact resistance depends on the specific alloy composition and environmental conditions.
- Surface finish: The surface finish of stainless steel can affect its corrosion resistance. Smooth, polished surfaces are generally more resistant to corrosion than rough surfaces because they minimize opportunities for corrosion initiation and facilitate easier cleaning.
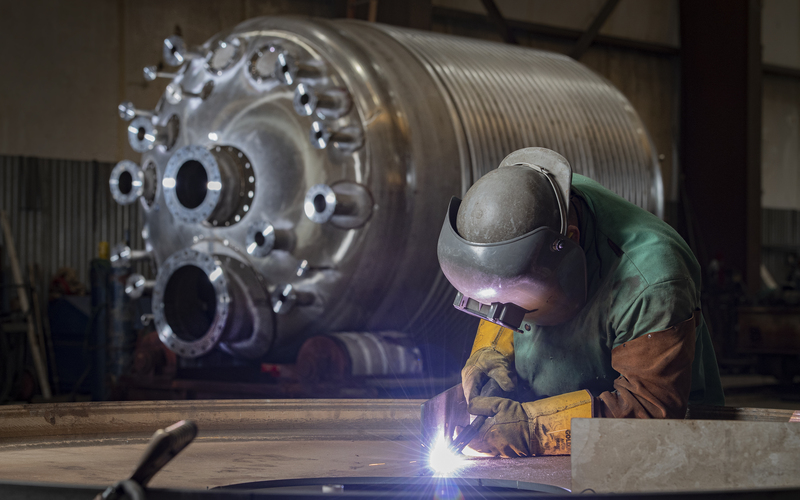

Custom Steel Tanks
At Tate Metalworks, we have over 50 years of experience field erecting and shop fabricating custom storage tanks and ASME Pressure Vessels for a wide range of industries and applications. Our commitment to quality and safety combined with our in-house engineering expertise, state-of-the-art fabrication equipment and experienced welders, ensures that your storage tank will meet your specifications and required reliability.
Custom Fabrication is Our Specialty
We specialize in building storage tanks to meet the unique needs of our clients and their industries. Our custom tank fabrication process features:

- Experienced in-house design and engineering
- In-house fabrication of all storage tank components, including rolled plate, nozzles, ladders, and platforms
- Storage tank size (shop-fabricated or field-erected)
- ASME Section IX certified welders with over 400 qualified welding procedures, including carbon steel, stainless steel, duplex stainless steel, and many other alloys
- ASME Section VIII Quality Control Program
© 2026 Tate Metalworks. All Rights Reserved|
Privacy & Cookies |
Site by ALINE, A Marketing Company


 Tate serves clients Nationwide, from our Headquarters in the Upstate of South Carolina.
Tate serves clients Nationwide, from our Headquarters in the Upstate of South Carolina.